Choose your favorite Ancient Egyption God or Goddess!
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 26, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/26/take-a-poll/
Ancient Egyptian Gods and Goddesses!
http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/gods/explore/main.html
http://ancienthistory.about.com/od/egyptmyth/tp/071507egyptiandeities.htm
http://egypt.mrdonn.org/gods.html
Video:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=78eg5fkBda4
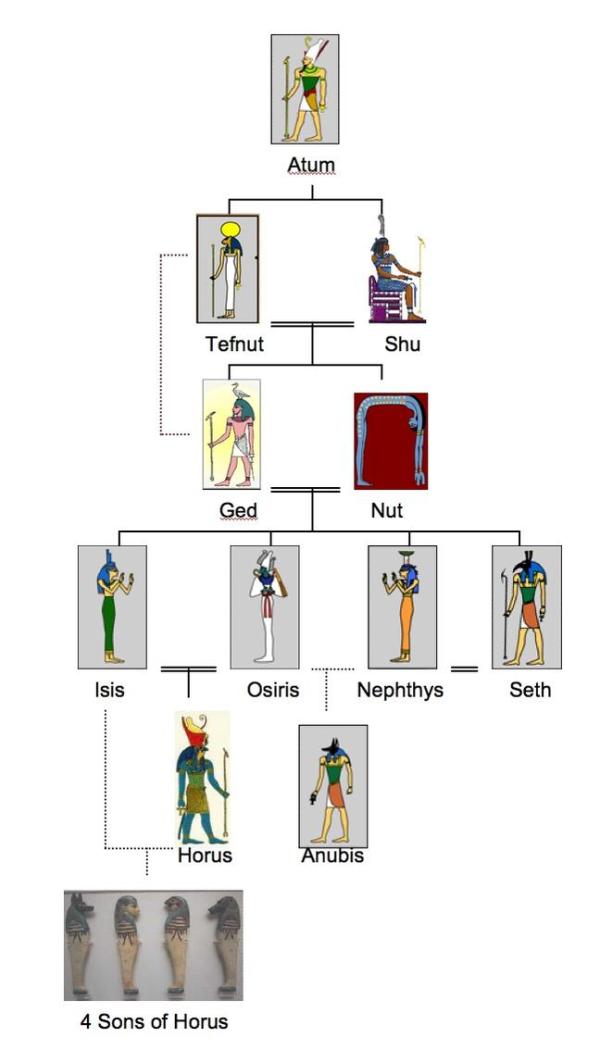
Ancient Egyptian Gods and Goddesses Family Tree
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 25, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/25/ancient-egyptian-gods/
Ancient Egyptian Stone Quarries
The unfinished obelisk, the largest known ancient obelisk, located in the northern region of the stone quarries of ancient Egypt in Aswan (Assuan), Egypt.
![By Ad Meskens (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) or GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrmeiners.files.wordpress.com/2013/10/1280px-unfinished_obelisk_07.jpg?w=300&h=225)
By Ad Meskens (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) or GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)%5D, via Wikimedia Commons
From http://mummies2pyramids.info/daily-life/stone-quarrying.htm :
Definition: A quarry, or ‘stone pit’ is a surface excavation for extracting stone. The ancient Egyptian Quarries were used for extracting building materials required for their extensive building projects.
More quarry information:
http://ancientegypt.me/quarrying-in-ancient-egypt/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stone_quarries_of_ancient_Egypt
Modern American Quarry:
“Old South Shaft Ore Quarry, Face of Tough-nut Mine, part of Town of Tombstone, Arizona. Dragoon Mountains, with Cochise Stronghold in background,” mammoth plate, by the American photographer Carleton E. Watkins. Courtesy of the Yale Collection of Western Americana, Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 22, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/22/ancient-egyptian-stone-quarries/
Ancient Egyptian Pyramids!
![By Ricardo Liberato [CC-BY-SA-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrmeiners.files.wordpress.com/2013/10/all_gizah_pyramids.jpg?w=300&h=199)
By Ricardo Liberato [CC-BY-SA-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)%5D, via Wikimedia Commons
Here is an interactive PBS website to let you explore the pyramids of Egypt:
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/pyramid/explore/
More pyramid info!
http://www.history.com/topics/the-egyptian-pyramids
http://egypt.mrdonn.org/pyramids.html
National Geographic Channel Video about how the Great Pyramid might have been built:
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 16, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/16/ancient-egyptian-pyramids/
Mummification!
When a person or animal dies bacteria on the body causes it to decompose, eventually leaving just the skeleton behind. Because Egyptians valued life after death they had an important ritual to protect the bodies. Ancient Egyptians believed they should provide their dead with a well-functioning body in the after life. Ancient Egyptians believed that they had a soul, which they called the KA. They believed the Ka was released from the body at the time of death. From then on the KA did not stay peacefully in one place. In order for the Ka to rest in the body at night, the body had to be preserved or mummified.
Research mummification:
http://www.kingtutone.com/mummies/mummification/
http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/mummies/home.html
Make your own mummy game:
http://kids.discovery.com/games/just-for-fun/mummy-maker
Video:
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 16, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/16/mummification/
Proper Heading!
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 14, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/14/proper-heading/
Pyramid Project Checklist!
![By Ricardo Liberato [CC-BY-SA-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrmeiners.files.wordpress.com/2013/10/all_gizah_pyramids.jpg?w=300&h=199)
By Ricardo Liberato [CC-BY-SA-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)%5D, via Wikimedia Commons
Ancient Egyptian Pyramid Project
(Homework)
1. The bottom square of your pyramid must be 10 inches on each side.
2. The side triangles must be 10”x10”x10” (equilateral triangle).
3. Answer this math question: What is the height of your pyramid?
4. The base of your pyramid (what your pyramid is placed on) must be 12”x12”.
5. This is your science question: What weather events caused the ancient pyramids to look like they do today?
6. This is your technology question: How did the ancient Egyptians move huge blocks to the top of the pyramid?
7. Your pyramid may be constructed of any materials. (It is not necessary to spend any money, but you may choose to do so.)
8. 9. 10. Write a paragraph answering these three questions.
1. Who helped you build this homework project? What did they do? How did you help each other? What materials did you use?
2. What was difficult about this project? What was easy? What was fun?
3. Did you choose to make you pyramid in the form of Ancient Egyptian completion or how they look today? Why?
Options
- Place your pyramid in any space on the 12”x12” base in case you wish to add landscaping.
- Create an interior of the pyramid with hieroglyphics. (5pts.)
- Write three sentences describing mummification. (5 pts.)
- Place a mummy in the pyramid. (5 pts.)
mm
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 7, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/07/pyramid-project-checklist/
King Menes and the Two Lands!
http://egypt.mrdonn.org/twolands.html
http://cuip.uchicago.edu/~bgresham/bgx3/menespg.htm
http://www.king-tut.org.uk/egyptian-pharaohs/menes.htm
Video:
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on October 7, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/10/07/king-menes/
Ancient Egypt “Prezi”
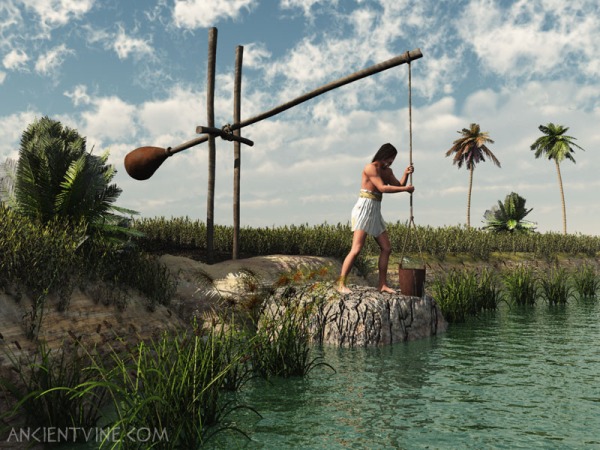

image courtesy of http://ancientvine.com/
Click on the link below to watch a Prezi presentation with lost of information
about Ancient Egyptian water technology:
http://prezi.com/pf3c9b1wnd0o/?utm_campaign=share&utm_medium=copy
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on September 24, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/09/24/798/
Hammurabi’s Code: Take a Poll!
Posted by Mr. Meiners Social Studies on September 18, 2013
https://mrmeiners.wordpress.com/2013/09/18/hammurabis-code-poll/



![Carleton Watkins [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrmeiners.files.wordpress.com/2013/10/tough_nut_mine_tombstone_arizona_by_carleton_e_watkinscarleton-watkins-public-domain-via-wikimedia-commons.jpg?w=300&h=214)